Common Speeding Violations
Depending on where you are traveling, speeding laws vary. Yet, most states have two different categories of speeding laws, or one law that addresses both types of speeding.
Specifically, speeding can refer to:
- Traveling over the posted speed limit, or
- Traveling too fast for conditions
For example, Texas law states that drivers “may not drive a vehicle at a speed greater than is reasonable and prudent under the conditions and having regard for actual and potential hazards then existing; and shall control the speed of the vehicle as necessary to avoid colliding with another person or vehicle that is on or entering the highway in compliance with law and the duty of each person to use due care.”
Louisiana law provides another example: “No person shall drive a vehicle on the highway within this state at a speed greater than is reasonable and prudent under the conditions and potential hazards then existing, having due regard for the traffic on, and the surface and width of, the highway, and the condition of the weather, and in no event at a speed in excess of the maximum speeds established by this Chapter or regulation of the department made pursuant thereto.”
Similarly, California statutes state, “No person shall drive a vehicle upon a highway at a speed greater than is reasonable or prudent having due regard for weather, visibility, the traffic on, and the surface and width of, the highway, and in no event at a speed which endangers the safety of persons or property.”
In addition, the California Vehicle Code sets out other provisions.
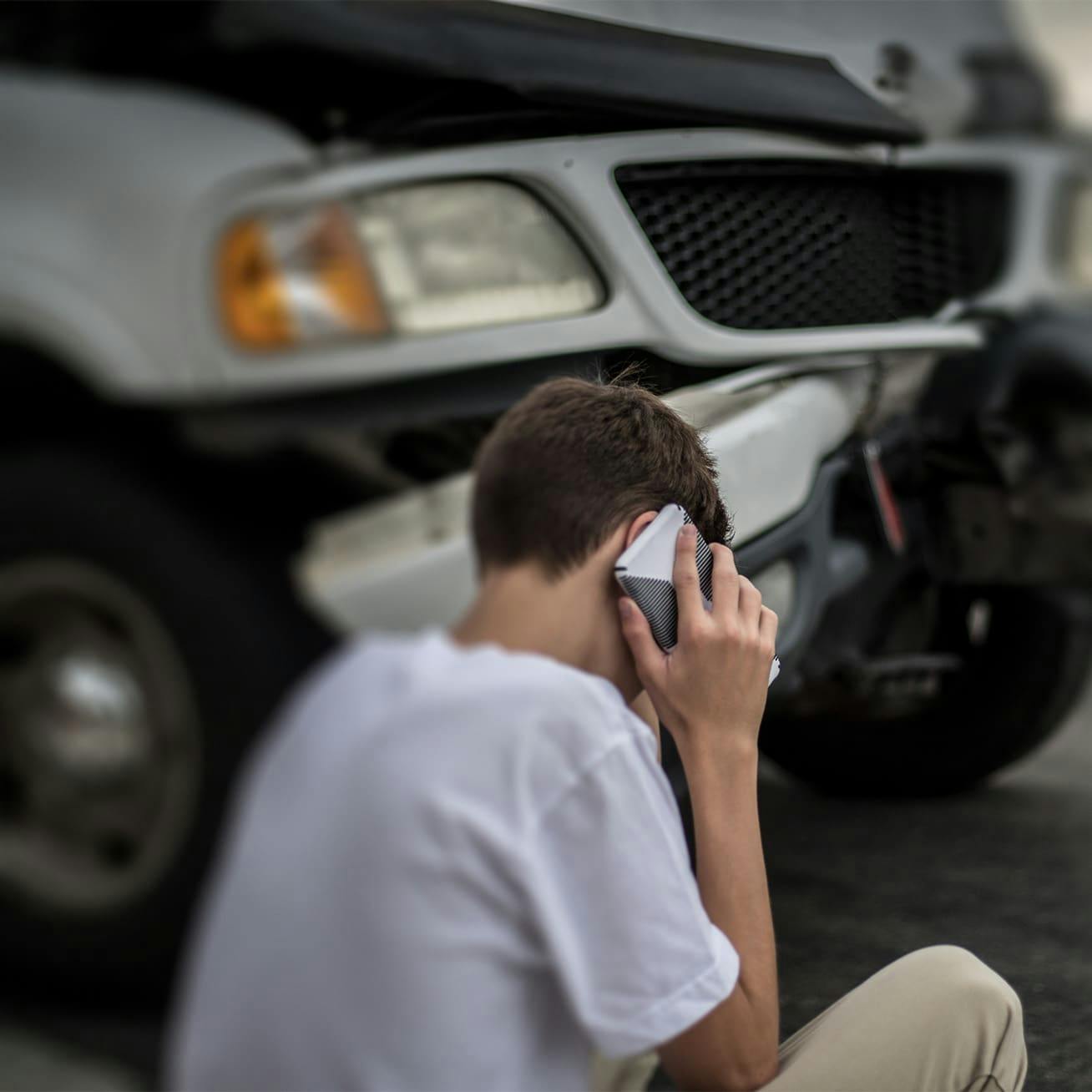
These broad speeding laws demonstrate the discretion law enforcement has to issue a citation in any situation they feel a driver is going faster than circumstances allow, regardless of the posted speed limit. It can also be challenging for a car accident victim to prove another driver was driving too fast for conditions. They will argue that they were within the posted speed limit, while your auto accident attorney can present evidence that they were, in fact, still speeding due to the conditions.
While some state laws are more explicit than others, situations where drivers are often expected to slow down include:
- Approaching an intersection
- Approaching a railroad crossing
- Approaching the top of a hill
- While driving on narrow and/or winding roads
- When pedestrians are present
- When driving in heavy traffic
- When road conditions or weather require a speed reduction
Law enforcement might issue a variety of speeding-related citations that carry various penalties, including fines and license suspension. Many states double fines for those who speed in construction zones. Those who speed in excess, typically defined as more than 20 miles over the posted speed limit, also face harsher penalties and might even receive a careless or reckless driving citation, especially if they committed other traffic law violations.
Penalties and fines typically increase when property damage or physical harm occurs as a result of speeding. When negligent drivers speed and cause the death of another driver or occupant, they might also face criminal vehicular manslaughter charges.
Do not mistake criminal charges for the legal relief you need. A criminal case aims to punish a speeding driver with fines, probation, or even jail time. However, this case does little to help you as an injured accident victim. Instead, you need to pursue your case in civil court to seek compensation, and you should do so with the help of a car accident attorney you can trust.